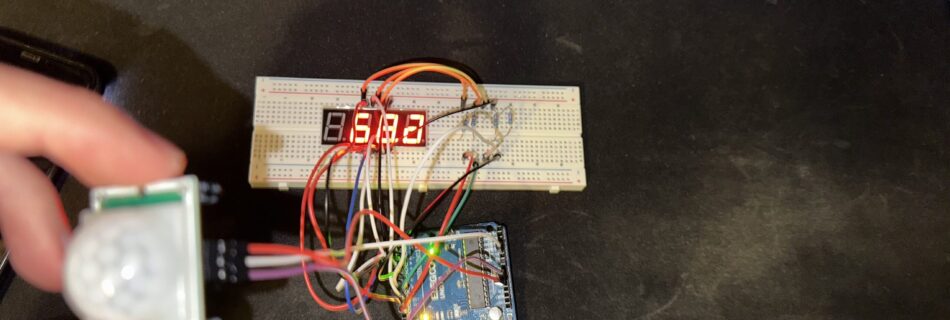
✋🏻 Project 8 – Apple Music Hand Tracker
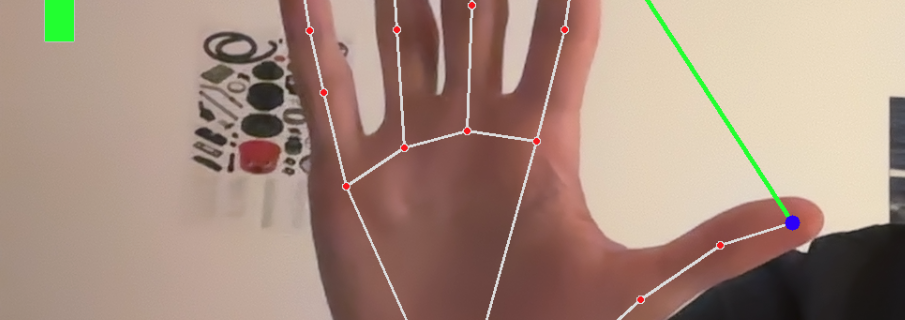
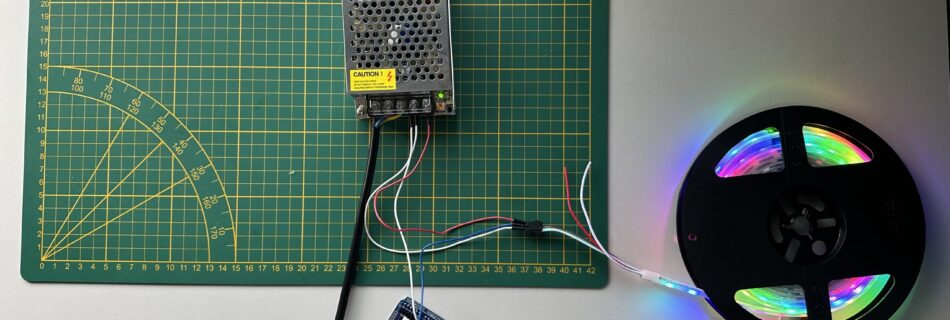
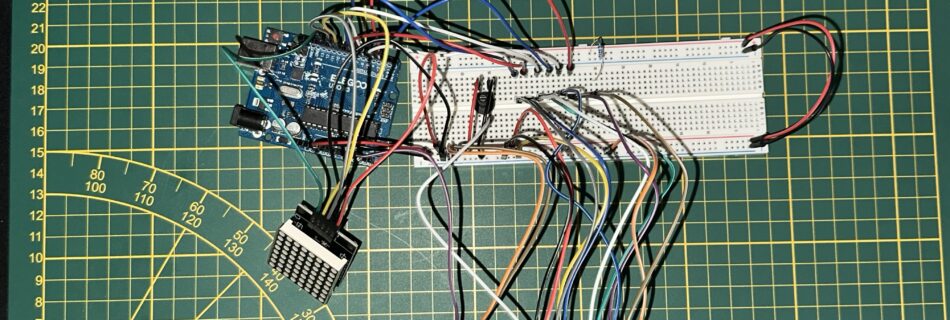
1. Presentation In this new project, after seeing people on Instagram controlling all sorts of things, such as photos and waves, with their hands, I did some research on the subject and discovered MediaPip, a library that uses machine learning to track the position of hands, faces, and the human body with a more or …